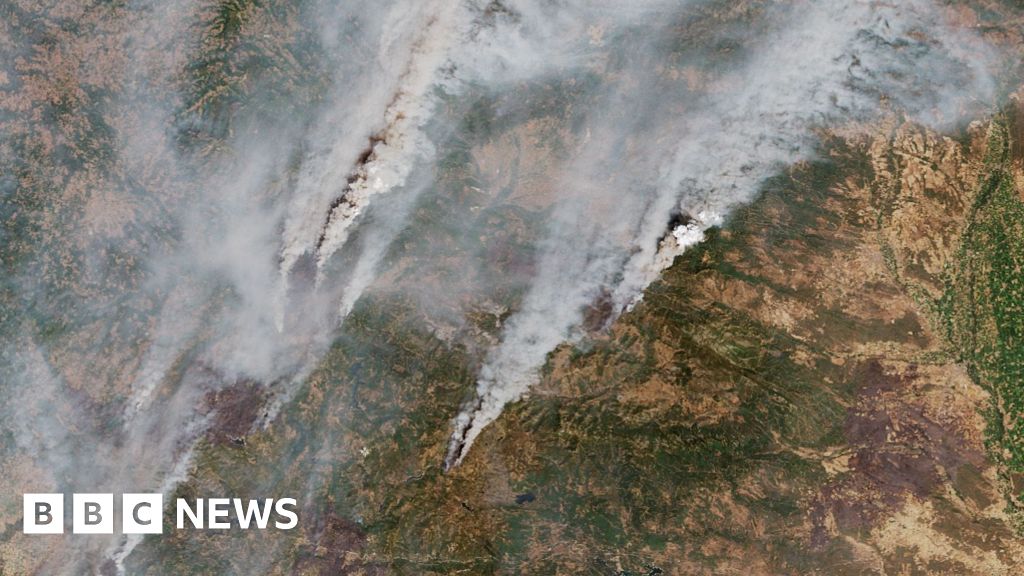
A record one million hectares - equivalent to about half the land area of Wales - have burned across the European Union so far this year, making it the worst wildfire season since records began in 2006.
Spain and Portugal have been hit especially hard, with roughly 1% of the entire Iberian Peninsula scorched, according to EU scientists.
The worsening fire season in the Mediterranean has been linked directly to climate change in a separate study by the World Weather Attribution group at Imperial College London.
Experts warn that more frequent and severe fires across Europe are likely to continue in the future.
More than two thirds of the area burned in the EU is in Spain and Portugal alone. In Spain, more than 400,000 hectares have burned since the beginning of this year up until August 26, according to the Copernicus European Forest Fire Information System (EFFIS).
This record is more than six times the Spanish average for this time period between 2006 and 2024.
Neighbouring Portugal has also suffered a record burn area of 270,000 hectares so far - almost five times the average for the same period.
The combined burn area across the Iberian Peninsula this year is 684,000 hectares - four times the area of Greater London, and most of it burned in just two weeks.
These fires have been concentrated in forested areas of northern Portugal and in Spain's north-western regions of Galicia, Asturias and Castile and León, impacting protected areas like Picos de Europa National Park and major routes on the Camino de Santiago pilgrimage network.
The events have triggered the largest known deployment of the EU civil protection mechanism's firefighting force.
Climate change makes the conditions leading to wildfires more likely. CO2 emitted by fires in Spain this year has reached a record 17.68 million tonnes, exceeding totals from previous years.
Firefighters continue to battle blazes across Europe, with climate change being a key factor in increasing fire frequency and severity. Experts emphasize the pressing need for better fire management techniques and reducing carbon emissions to mitigate future risks.